- Categories: Flow, Kanban, Scrum with Kanban
- Tags: Kanban, Kanban Basics, Limiting Work in Progress, Professional Scrum with Kanban, Scrum, Scrum With Kanban, WIP
- Author: AgileSparks
Co-Creating and teaching the new Scrum.org Professional Scrum with Kanban class has given me an opportunity to get back to geeking out on WIP limits, flow metrics, and all things Kanban. And it’s been fun!
One of the key Kanban practices is Limiting Work in Progress. If you want to be pedantic, actually what this practice aims for is Reducing and stabilizing Work in Progress. This improves flow, provides predictability, and is actually even more important for creating a pull-based Kanban system than visualizing your workflow using a Kanban board. I worked with several clients who limited their WIP but didn’t use Kanban boards. One could argue that maybe this practice deserves to be first in the list of Kanban practices, ahead of Visualization.
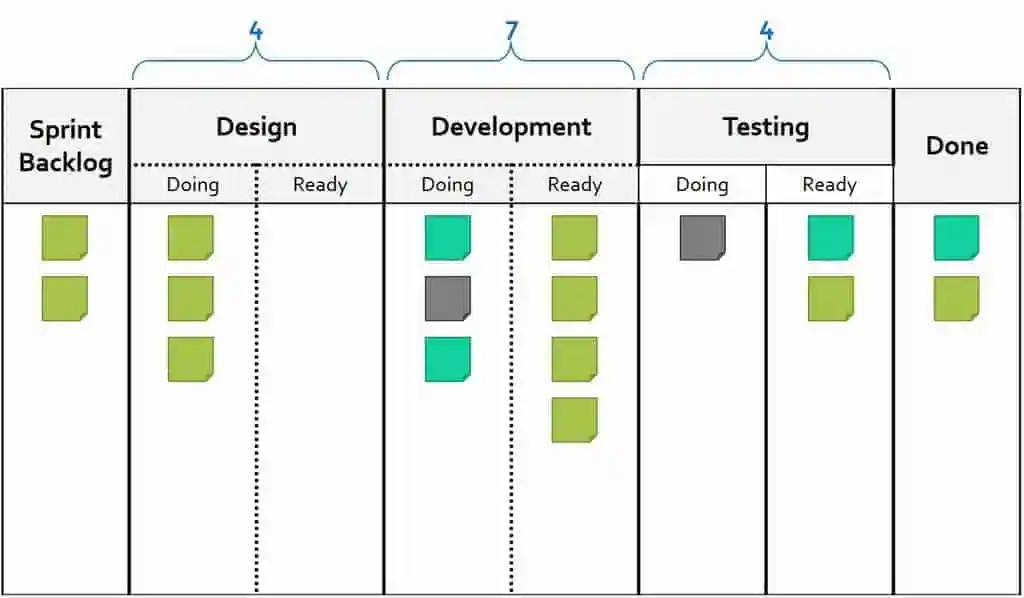
Anyhow, when a Scrum Team implements Kanban they should definitely figure out how to limit and reduce their Work in Progress. This is a key part of their definition of “Workflow”. First of all, when we say flow we mean flow of valuable items – so flow of PBIs (rather than tasks).
Now, a question comes up: Who should define the WIP Limit? Let’s assume the team is using Kanban to improve the Sprint flow by visualizing and managing flow in the Sprint Backlog. Sprint Backlog is owned by the Development Team so it would make sense for them to own their workflow and specifically the WIP limits in this case.
What if the team is using Kanban from a more holistic perspective, starting from the Product Backlog and including refinement work as well? In this case, it would be the Scrum Team that would own the workflow and therefore would need to discuss WIP limits.
Now, what if the Dev Team actually wants to involve the Product Owner in their Sprint flow – e.g. to review and accept a story during the Sprint before it goes through testing? Who decides whether to do this? Who owns the Sprint Backlog in this case? I think it is the Scrum Team.
Ok, so we understand who defines workflow and therefore WIP limits. Now let’s assume a team is mid-Sprint and there’s an important valuable item the Product Owner wants to add to the Sprint Backlog. It is aligned with the Sprint Goal. The team is currently at its WIP Limit. Could they add this item? Should they? What needs to happen to the WIP limit?
My take on this is that first of all a decision needs to be made on whether to pull this item into the Sprint Backlog. This discussion isn’t related to Kanban at all. It is a core Scrum question and the answer is that it is up to the team to agree to pull a new item into the Sprint Backlog. The Sprint Goal can be used to assess how aligned this item is with the current focus.
In case the item is pulled into the Sprint Backlog, then the Dev Team needs to figure out whether they can actually start it right away. This depends on the WIP limits and the current WIP. If the team is at their WIP they shouldn’t pull in that new item until some room frees up. If their backlog items are pretty small, an empty WIP slot will free up pretty quickly. If items are big, it can take a while.
The longer it might take to get a normal pull slot ready, the more pressure there might be to actually expedite this card. What is expediting? going beyond the current WIP limits and pushing this item along on top of the existing flow. The typical way to do this is NOT to change the WIP limit definition but to go above WIP and note a WIP exception. These exceptions can then be a topic for inspection and adaptation come time to retrospect.
In general, I don’t recommend changing WIP limits on a whim just because there seems to be a need during the Sprint. I’d rather see an exception and discussion rather than hide the problem under a policy change. Most of the time, Scrum Teams should adjust WIP limits during the Sprint Retrospective out of an attempt to create a better flow strategy, not a way to manage at the tactical level. This is similar to the definition of Done. We don’t change the definition of Done during a sprint just because we have a problem creating a Done Increment. We note the exception, maybe even fail to create a really Done Increment, and we discuss the definition during our Retrospective.
One last thing to note about limiting WIP is that while we typically talk about limiting WIP as per-lane constraints on your workflow, this is actually just one specific way to do it. You could limit the amount of work in progress per person, per the entire team throughout their workflow, or actually, you could limit WIP by time. E.g. “we won’t work on more than 10 items this week”. Hey – that sounds familiar! #SprintForecast.
NOTE: Updated to emphasize that we want to limit WIP by valuable PBIs (rather than tasks). Thanks, Giora for suggesting to make that explicit.
